Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Hiroaki*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 168, p.211 - 222, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:47.52(Chemistry, Physical)Microstructural and mass transport properties of compacted Na- and Cs-montmorillonites with different swelling properties were investigated by combining 3D microstructure analysis using nanofocus X-ray CT and diffusion measurement of HDO. The X-ray CT observations indicated that macropores in the dry state of compacted Na-montmorillonite are filled with gel phases, and the grain sizes of clay particles shifted toward smaller values through the saturation and swelling processes. By contrast, no gel phase and no decrease in the grain and pore volumes were observed for saturated Cs-montmorillonite. The geometrical factors of the macropores including tortuosity and geometric constrictivity of saturated Cs-montmorillonite determined by the X-ray CT was consistent with the corresponding values derived in the HDO diffusion test. In the case of Na-montmorillonite, the larger differences between the geometric factors evaluated by the X-ray CT and the diffusion tests can be explained by the electrostatic constrictivity factor and the additional geometrical factors in gel phase and interlayer that are smaller than the detection limit of the X-ray CT.
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditionsSawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.267 - 278, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.47(Chemistry, Physical)The dependences of the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite on activity of OH (a
(a -) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (
-) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (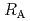 ) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as
) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as 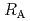 = 10
= 10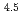 (a
(a -)
-)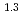 e
e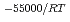 , was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures:
, was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures: 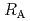 = 3500 (a
= 3500 (a -)
-)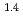 e
e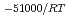 . The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a
. The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a - in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a
- in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a - is achieved somehow.
- is achieved somehow.
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Applied Clay Science, 123, p.148 - 155, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:74.44(Chemistry, Physical)The pore distribution of water-saturated compacted clay (Na-montmorillonite at 0.8 and 1.4 g/cm saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using
saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using  H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature
H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature  H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with
H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with  H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (
H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (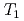 ) and transverse relation times (
) and transverse relation times (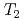 ) at -10
) at -10 C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm
C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm .
.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Ito, Tsuyoshi; Suyama, Tadahiro
no journal, ,
The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model was applied for systems coexisting multispecies Sr (divalent cation Sr and neutral SrSO
and neutral SrSO (aq)) in compacted montmorillonite. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Sr in compacted Na-montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m
(aq)) in compacted montmorillonite. Effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Sr in compacted Na-montmorillonite (dry density of 800 kg/m ) saturated with three types of Na
) saturated with three types of Na SO
SO solutions (0.05, 0.1, 0.5 M) were measured by the trough-diffusion method. The De and Kd values decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The De for multispecies Sr was determined as the harmonic weight-average considering the two species distribution and their log De values, based on comparison with reactive-transport calculations using the PHREEQC. As a result, the De trend could be quantitatively express by the ISD model considering multispecies contributions. The thermodynamic sorption model considering ion exchange reactions could provide reasonable account of Kd trend as functions of salinity.
solutions (0.05, 0.1, 0.5 M) were measured by the trough-diffusion method. The De and Kd values decreased drastically with increasing porewater salinity. The De for multispecies Sr was determined as the harmonic weight-average considering the two species distribution and their log De values, based on comparison with reactive-transport calculations using the PHREEQC. As a result, the De trend could be quantitatively express by the ISD model considering multispecies contributions. The thermodynamic sorption model considering ion exchange reactions could provide reasonable account of Kd trend as functions of salinity.
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
no journal, ,
1H NMR relaxometry was applied for investigation of pore structure in compacted saturated montmorillonite with different salt concentration. The samples compacted to dry densities of 0.8 and 1.2 g/cm were saturated with pure water, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, and 1.0 M NaCl solutions. Population of water in different hydrated layer corresponding to 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layer was estimated from longitudinal relaxation distributions. The population of water in 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layers changed as a function of NaCl concentration. The threshold to discriminate between inter- and intra-layer water is 3 hydrated layer, which is questionable from existence of 4 hydrated layer revealed by modelling of X-ray profile. The amount of water in 1- and intra-layer were negligible small for all conditions at dry density of 1.2 g/cm
were saturated with pure water, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, and 1.0 M NaCl solutions. Population of water in different hydrated layer corresponding to 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layer was estimated from longitudinal relaxation distributions. The population of water in 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layers changed as a function of NaCl concentration. The threshold to discriminate between inter- and intra-layer water is 3 hydrated layer, which is questionable from existence of 4 hydrated layer revealed by modelling of X-ray profile. The amount of water in 1- and intra-layer were negligible small for all conditions at dry density of 1.2 g/cm . On the other hand, water in 2-hydrated layer was decreased instead of increment of water in 3-hydrated layer.
. On the other hand, water in 2-hydrated layer was decreased instead of increment of water in 3-hydrated layer.